Back in the summer of 1993, I was on a road trip around the western United States with three of my kids and while staying in Salt Lake City we decided to take in a new movie that had just come out, Jurassic Park. I am sure most of you have seen it or at least heard of the dinosaurs gone wild adventure. It was the greatest GMO experiment, science fiction in that day but science fact today. They found a mosquito captured in a ball of amber and extracted dinosaur DNA from the blood in the belly of the bug, cloning it into true living dinosaurs for an island theme park. This movie hits on several things we will be looking at today in our blog, the dinosaurs and DNA. 
First let’s go back to the last blog entry about the Cambrian Explosion that occurred about 540 million years ago. Since then, there have been five major mass extinction events with the last one happening about 65 million years ago when the dinosaurs became extinct. This extinction was possibly due to two catastrophic events occurring one right after the other, a massive volcanic eruption followed by a gigantic asteroid slamming into the Yucatan peninsula. These two events covered the earth with hundreds of feet of ash and soot - laying down a geological layer that would wipe out the dinosaurs and produce large oil and gas pockets. Without the mass extinction of these fierce reptiles, we would not have the oil that has driven our industrial revolution over the last 200 years. God used all of these events for a purpose. People often ask if God just wanted to make man, why so much wasted space or life or whatever, but He had a reason and a purpose for all that He did in His creation. All of it was necessary, even though we might not know why now - Prov 25:2 (KJV) - It is the glory of God to conceal a thing: but the honour of kings is to search out a matter.
So now today we will look at what makes life so special. Just in terms of advanced life forms, including man, the physical being of the structure of life is extremely complex. We learn new things daily about how wondrous the cell is and how bringing millions and billions and trillions of cells together, a functional being results. All multi-celled life forms have an array of cell types that function in different ways but come from one cell. Even the simplest of organisms is indeed complex.
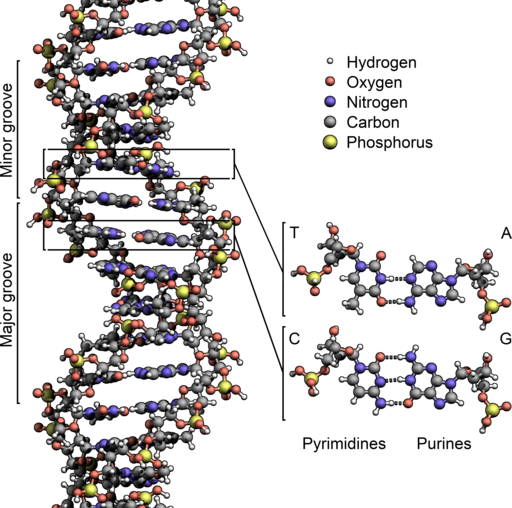
But let’s go back to the DNA part of the story first. Human DNA has a sequence of over 3 billion letters (A-Adenine, G-Guanine, C-Cytosine and T-Thymine). Only 5% of our DNA contains the codes for the 10,000+ proteins used in our bodies. The rest was once considered junk DNA but science has now determined that up to 80% of this remaining DNA actually controls how and when the proteins are made and what the cell form will be. The DNA string is wrapped up tightly in coils and stored in every single cell in our bodies. This allows the 3 billion base pairs in each cell to fit into a space just 6 microns across (the cell nucleus). If you stretched the DNA in one cell all the way out, it would be about 6 feet long and all the DNA in all of your cells put together end to end would be about twice the diameter of the Solar System.
Biologists must constantly keep in mind that what
We see was not designed, but rather evolved.
Frances Crick - referencing the DNA double Helix
DNA stores all the information to make you, in each and every cell. In fact, science can now tell a lot about your origin and ancestry by looking at your DNA. You can even send in a kit with a sample of your tissue and get back an analysis that will tell where your ancestors came from. Science has even been able to get DNA from fossils and sequence it and trace the lineage of the fossil. Neanderthal man is a case in point. Once thought to have been our direct ancestor, he has now been shown not only to not be directly related but actually from a different chain in the genus Homo. DNA testing shows that humans have some Neanderthal DNA but possibly it comes from interbreeding or a common ancestor farther back. DNA shows most, if not all mankind (homo sapiens) has one ancestor (Adam or mitochondrial Eve?).
DNA has built-in mechanisms to prevent errors in coding - there are 64 possible 3 nucleic acid strings (such a string specifies one amino acid in the protein being formed) and only 20 amino acids used in our genetic code to produce proteins. Most amino acids have more than one three character code and the extra sequences are used to help with error correction by preventing minor mutations from changing the resulting protein.
But it is not fool proof. Even a single amino acid error can sometimes produce a disorder as in Sickle Cell disease. The DNA mutation of a single nucleotide of the hemoglobin gene results in glutamic acid being substituted by valine at position 6 in hemoglobin's beta protein strings of 146 amino acids (hemoglobin is made up of 2 alpha and 2 beta protein strings totaling 574 amino acids). This occurs when the A (Adenine) in the DNA three letter sequence GAG, which translates to glutamic acid in the protein, is substituted with T (Thymine), changing the sequence to GTG which translates to valine. This is normally a benign mutation, causing no apparent effects on the structure of hemoglobin in conditions of normal oxygen concentration. What it does allow for, under conditions of low oxygen concentration, is the sickle formation of the red blood cells due to the genetically different hemoglobin molecule whose shape is changed by this one amino acid error.
Science now can modify the DNA of a single cell organism, typically a bacterium, and have it produce a new or modified protein. This is called recombinant DNA (rDNA) technology. A great example using this technology in the healthcare field is the development of rDNA human insulin. Previously insulin for human use was extracted from beef and later from pork. Although these worked, they could cause allergic reactions. Insulin is a protein made up of two chains totaling 51 amino acids - beef has three different amino acids and pork has one compared to human insulin and yet our bodies can tell the difference. Now with rDNA produced human insulin, these adverse effects are a thing of the past.
 Francis Crick, the scientist who deciphered the double helix of DNA, said of his work: "Biologists must constantly keep in mind that what we see was not designed, but rather evolved." He also said: "An honest man, armed with all of the knowledge available to us now, could only state that in some sense, the origin of life appears at the moment to almost be a miracle, so many are the conditions which would have to have been satisfied to get it going."
Francis Crick, the scientist who deciphered the double helix of DNA, said of his work: "Biologists must constantly keep in mind that what we see was not designed, but rather evolved." He also said: "An honest man, armed with all of the knowledge available to us now, could only state that in some sense, the origin of life appears at the moment to almost be a miracle, so many are the conditions which would have to have been satisfied to get it going."
Scientists have tried to take this one step farther and create life in the lab. They made a synthetic organism, but it was no primordial goo that happened to come alive. It took scientists hundreds of hours using computers and other very sophisticated equipment, cost over $40 million dollars and 15 years of work. Certainly not a simple process and the end result was not alive. Although it did function in some respects, it could not produce, or reproduce, the complex molecules needed to sustain and duplicate life.
Doctor David Deamer, one of the scientists involved in this work, published an article where he listed the following 12 specific steps needed to create the simplest form of life.
Defining artificial life:
What would such a system do? We can answer this question by listing the steps that would be required for a microorganism to emerge as the first cellular life form on the early Earth:
- Boundary membranes self-assemble from soap-like molecules to form microscopic cell-like compartments.
- Energy is captured by the membranes either from light and a pigment system, or from chemical energy, or both.
- Ion concentration gradients are maintained across the membranes and can serve as a major source of metabolic energy.
- Macromolecules are encapsulated in the compartments but smaller molecules can cross the membrane barrier to provide nutrients and chemical energy for primitive metabolism.
- The macromolecules grow by polymerization of the nutrient molecules.
- Macromolecular catalysts evolve that speed the growth process.
- The macromolecular catalysts themselves are reproduced during growth.
- Genetic information is encoded in the sequence of monomers in one set of polymers.
- The information is used to direct the growth of catalytic polymers.
- The membrane-bounded system of macromolecules can divide into smaller structures that continue to grow.
- Genetic information is passed between generations by duplicating the gene sequences and sharing them among daughter cells.
- Occasional mistakes (mutations) are made during replication or transmission of information so that the system can evolve through natural selection.
After considering this list, he said: "Looking down this list, one is struck by the complexity of even the simplest of life. This is why it has been so difficult to ‘define’ life in the usual sense of a definition – that is, boiled down to a few sentences in a dictionary. Life is a complex system that cannot be captured in a few sentences, so perhaps a list of its observed properties is the best we can ever hope to do." (emphasis mine).
What did the cell look like to scientists when Darwin first proposed evolution? It was protoplasm and a nucleus. What sparks a single cell to split and differentiate into a myriad of cell types - in humans, hearts and lungs and brains and... Is it just the pressure of "survival of the fittest (natural selection)?” How does the DNA know that for this cell in this place it needs to be a nerve cell? All cells carry the full gene complement to produce any cell in the body but surroundings somehow tell a cell to be special.
Life is extremely complex. Could this all happen by chance, by the pressure of natural selection, in just 3.8 billion years, with all that the earth has gone through during that time? Science says this happened by chance, not because they know it does but because they have no other theory for it, and they cannot say God because He does not exist in the physical realm scientifically, nor can He be proven or dis-proven by science. In my mind he can and does exist and it is for each of us to decide for ourselves what we believe. The evidence is there.
With this, we are just scratching the surface. The cell is full of complex systems, not just the DNA that directs it or the proteins that run it. There are numerous other features, such as mitochondria and ribosomes, and numerous other chemical reactions, such as the Krebs cycle and active transport of nutrients, that must function to get the job of life done. God is amazing!
Romans 1:20 (NIV) - For since the creation of the world God’s invisible qualities—his eternal power and divine nature—have been clearly seen, being understood from what has been made, so that people are without excuse.



